Thalassemia
Thalassaemia refers to a group of inherited blood disorders that affect the production of haemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
People with thalassaemia either produce insufficient haemoglobin or none at all, leading to severe anaemia.
There are 6 types, thalassaemia trait/minor, haemaglobin H disease, alpha thalassaemia, sickle beta thalassaemia, beta thalassaemia intermediate and beta thalassaemia major.
Knowledge and expertise in thalassemia
Most individuals with thalassaemia experience health issues from infancy including bone fragility. Some patients may experience delayed growth, weak bones (osteoporosis), and reduced fertility.
Regular blood transfusions are used to treat anaemia in Thalassaemia, and this can lead to excess iron accumulation in the body, affecting the heart, liver, and hormone levels.
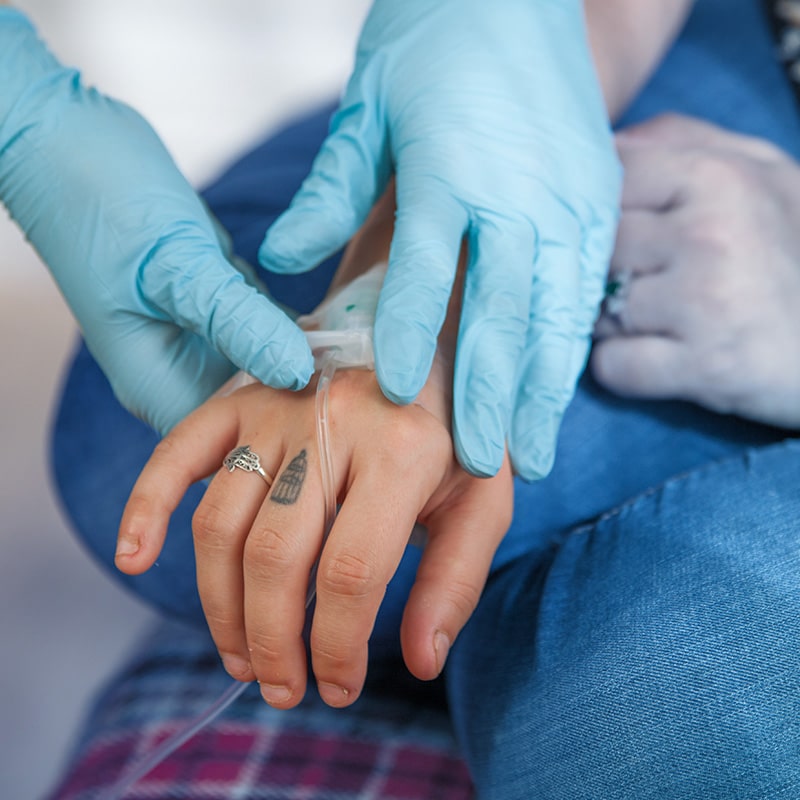
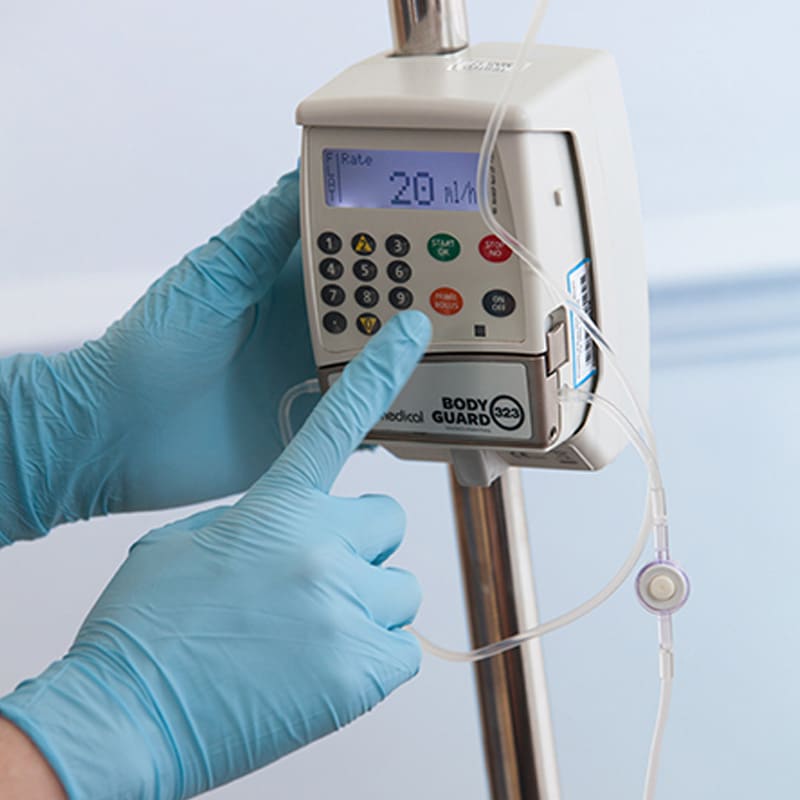
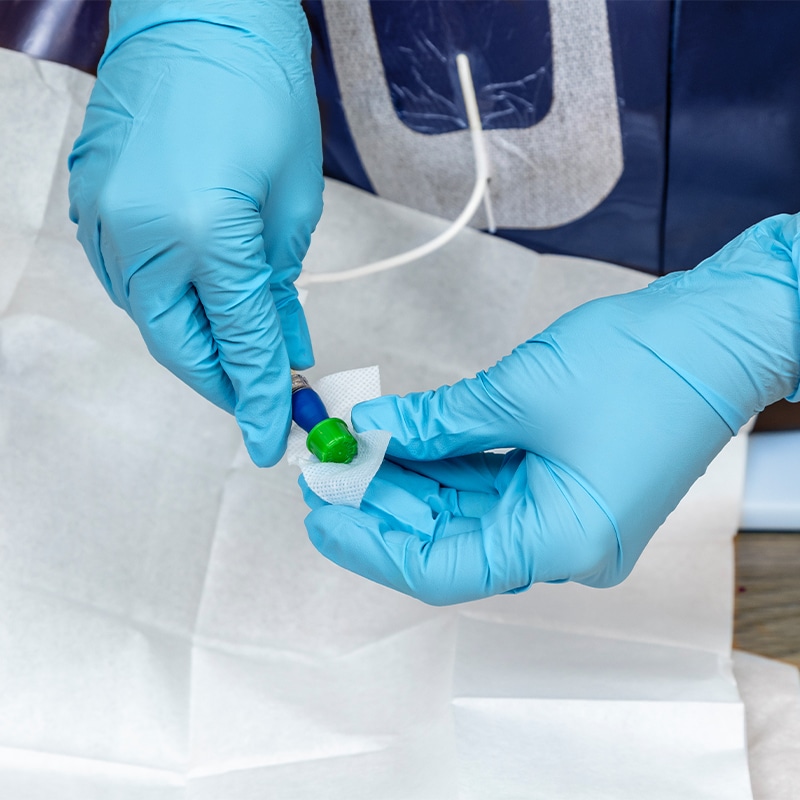
People who encounter this side effect of thalassaemia treatment may then need to receive chelation therapy, which is where we can step in to help treat with delivery of and administration training of desferrioxamine.

We know how to help patients live alongside thalassaemia
Our clinical specialists visit thalassaemia patients at home to train them on how to administer their compounded treatment. Every day we help thalassemia patients manage their condition themselves.
Our training puts patients back in control of their condition and their life allowing them to live more independent fuller lives.

Carriers of thalassemia
Carriers of Thalassaemia are generally healthy, you may not know you are a carrier unless you are tested for the condition.
Although Thalassaemia is not one of the conditions tested for in the NHS New Born Blood Spot screening programme, babies with beta Thalassaemia major will be identified during the process.

Learn more about our other nurse led treatments
Every day, our specialist clinical teams deliver a wide range of clinical therapies, for patients and their families.